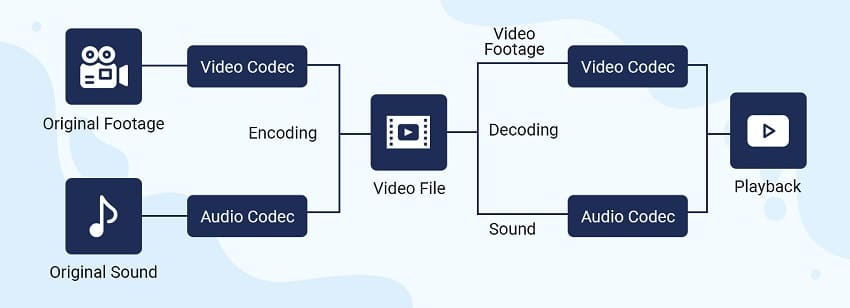
Container + Codec
Have you ever heard of containers and codecs? Basically, a video is made of these two components and to work they must coincide. In simpler form, Video = Container + Codec. In this, a video contains a video format and metadata(video and audio). The Codec is an unzipped format that is used to read the video making it a major component.
On the other side, a container is like a compression package that contains audio tracks, video tracks, graphics, visual images, and other media. It helps to distinguish the different data types. It is also referred to as the format of a file. The interlink is in that a codec is a decompression tool that can read these packets and offer faster transmission. Once, a file is made smaller and in a readable manner, it is easier to read. The codec function of decoding takes the compressed video files and makes them usable for playback or video editing.
Container (file extension)
A container is like a box that contains your video, audio, media, and metadata. It can also be termed as a file extension because they are often seen as file names. For example AVI. A video file normally contains a container with video data in a decoding format alongside the audio coding format. The container can also contain synchronization information, subtitles, and title. A container format is part of computer files that exist to allow multiple data streams to be embedded in a single file.
Codec (compression)
A codec deals with compressing your file either in the lossless or lossy format. The quality can’t easily be perceived by the human eye but can make visuals look grainy, flat, or muffled. To compress a file you must have a corresponding codec. Once it compresses your video, it can be stored and played back. The most common codec includes h.264 often used for high-definition digital video and distribution of video content. The one that compresses is termed as an encoder and the decompressor is a decoder. It ultimately affects the size of the video files, sound quality, and picture quality. This makes t easier to view a file.
What is Bitrate?
Bit rate is the number of bits conveyed or processed per unit of time. The bit rate is often quantified using the bits per second unit (bit/s). The higher the bit rate, the better the picture quality in units of bp/s, kb/s, or mb/s.
This is the number of bits per unit of time that media plays continuously. It also describes the rate at which bits are transferred from one location to another in a given time.
Different Video Formats
1. Mp4
It is one of the earliest digital video file formats that was introduced in 2001. Most of the digital platforms and devices support MP4. An MP4 format can store audio files, video files, subtitles, still images, and text. It also provides high-quality videos while maintaining small file sizes. It also allows streaming over the internet.
MP4 is an international standard for audiovisual coding. The current version MPEG-4 Part 14 was released in 2003. MP4 is considered a digital multimedia container format. This is because it contains a bunch of data that has been compressed. The standard specifies how the data is stored within the container itself. It can be opened by almost all video players and supports a wide range of devices. It also has a high compression ratio, contains metadata, and lower resolution than MKV.
2. MOV. QT (QuickTime format)
MOV is a video file format designed by Apple to support the QuickTime player. MOV files tend to contain videos, audio, subtitles, time codes, and other media types. It is compatible across different versions of Quick Time Player both for Mac and Windows. It is a high-quality video format hence consumes more memory space on a computer. It uses the concept of the track to store data.
3. FLV, F4V, SWF (flash format)
FLV is a file format used by the Adobe Flash Player or Adobe Air. It is among the most popular and versatile video formats supported by all video platforms and browsers. It is also a good choice for online video streaming platforms like Youtube. They also have a relatively small file size which makes them easy to download. It has been long the standard video format used by nearly all embedded video on the internet. However, many streaming services are opting for HTML5.
4. AVI
AVI stands for Audio Video interlace and contains both audio and video data in a file container. This allows synchronous audio with video playback. It was one of Microsoft’s old digital video format. Also, AVI supports multiple streaming formats although the features are seldom used. It uses less compression than other video formats such as MOV. Hence, large file sizes of up to 2-3GB per minute of video. It can be a major problem for users with limited storage space. You can also create AVI video files without any compression hence retaining its great quality. Also, this eliminates the use of codecs in video players.
5. WMV/ASF
ASF is a successor of the AVI format and is known as WMV codec. WMV was designed by Microsoft and is used in windows media players. It provides small file sizes with better compression than MP4. This makes it popular for online video streaming. WMV video files are most suitable for selling video content online or through HD DVD and Bluray Discs. It is one of the most recognized video file formats that support cross platforms. WMV allows large files to be compressed or reduced in size for better support to use over the network while still protecting the quality.
6. AVCHD
AVCHD means Advanced Video Coding High definition that was designed by Panasonic and Sony for digital camcorders. It can be compressed to a small size while preserving quality. It has evolved with the latest version supporting 3D videos. It is a file-based format for the digital recording and playback of high definition video. It is h.264 and Dolby AC-3 packaged into the MPEG transport stream. By using the AVCHD format you can burn high definition video to a standard DVD and play it in a blu-ray disc player. An AVCHD file also consists of recorded audio and video with subtitles and another ancillary steams. It supports a variety of video resolution and scanning methods.
7. MKV (matroska)
MKV is a file format that incorporates audio, video, and subtitles in a single file. It was developed to be future proof. MKV containers support any video or audio format. Hence really adaptive and easy to use. It is also known as Matroska Video file in full. It was first developed as an open standards project meaning it is open-source and completely free for anyone who wants it for personal use. MKV files are multimedia container formats. It features fast seeking chapter, menu, and metadata support. It offers error recovery, subtitle recovery, and online streaming compatibility. It means that it is possible to put an entire movie with multiple sounds and subtitle tracks and also a movie thumbnail into a single file.
8. WEBM/HTML5
WebM is an open, royalty-free, and media file format designed for the web. The WebM defines the file container structure, video, and audio formats. It consists of video streams compressed with VP8 or VP9 video codecs and audio streams. The WebM file structure is based on the Matroska container. HTML5 is Google’s format for building the web. It is free and popular on many websites like Twitter, YouTube, and much more.
9. 3GP
It is a multimedia container format that is defined by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) for 3G UMTS multimedia services. It is an internet and 3G communication transmission of video audio format, and small video files. However, it may produce low-quality videos. It was developed to save on space, bandwidth, and data usage. It is the required standard format for media files using Multimedia Messaging Service(MMS). Hence great for mobile devices.
10. Realvideo
RealVideo is usually paired with Real Audio and packaged in a Real media container. It is suitable for use as a streaming media format. This is the one that is viewed while being sent over the network. The file format for video streaming may be structured as a single stream where the content is represented in one data stream. The streams can be encoded as a constant bit rate or for constant visual quality. It is also a suite of proprietary video compression formats developed by Real Networks
11. MXF
MXF means Material Exchange format and is a container format for professional digital video and audio media. It can also carry multiple video and audio streams and is ideal for making videos. Also, it can easily edit metadata but not easy to repair when damaged. A typical example is like delivering advertisements to TV stations and tapeless archiving of broadcast TV programs. MXF has full timecode and metadata support. MXF was developed to carry a subset of the Advanced Authoring format data model under a policy of zero divergence directive. It also can contain several different compression formats in a single file making it a standard of all digital video formats. It can also be converted into AVI or MOV.
12. CinemaDNG
CinemaDNG is Adobe’s industrial standard for digital video file beds. It is the most efficient way to save raw video materials. It is a great pick for great color space and frame rates. It caters to a set of movie clips, raw video images, audio, and metadata. CinemaDNG supports stereoscopic cameras and multiple audio channels. It is designed to store high-resolution video streams in camera raw format and adds less than 1KB overhead per image. The CinemaDNG files typically require half the storage space of DPX files.
Comparison and Compatibility
Conclusion
The different video file formats can be used in various ways. Hence, if you are creative you need to know the right video editing tool you can use. This is also with the right video format you save it with. You can choose a format that limits who can view the file if it has a few compatible media players. They also have different pros and cons that will help you decide on the best video file format for use.